Progress in Research on DUX4 Expression in Human Embryonic Genome Activation
The gene that is very first turned on in the fertilized egg cell is called DUX4. It starts a cascade of turning on genes in the early embryo in a specific and highly regulated manner. Little by little, this gene activation results in the specialization of all cell types in the human body.
In these studies, the researchers found out that DUX4 works by not only activating genes, but also changing the way the DNA in the chromosomes is wound open and activating a large number of subtle gene regulatory elements, so-called enhancers. Which other proteins DUX4 is binding to for gene regulation were also studied. Interestingly, when the researchers prevented DUX4 activity in fertilized human egg cells, cells in such early embryos continued to divide normally until day 3, or 8-cell-stage, until which time the study was extended.
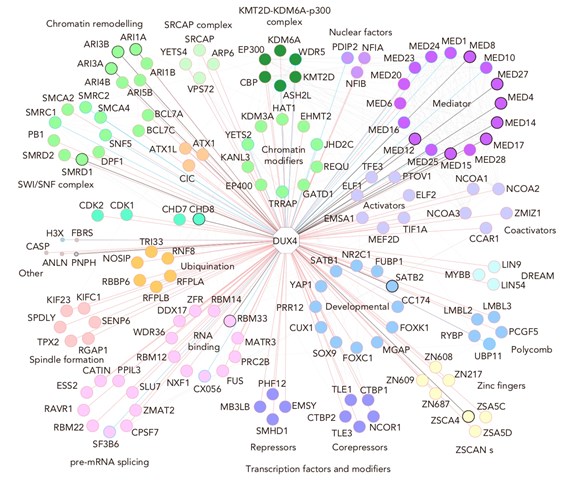
Fig 1. Transcription factors and modifiers.
The key role of DUX4 in activating the embryonic program prompted us also to study if it could reprogram later embryonic stem cells, representing nearly a week-old embryo, back to the earlier developmental stage. To test this, the researchers turned DUX4 artificially on in embryonic stem cells for only a short period of time, 15 minutes, as we learned that cells would not survive if DUX4 was continuously on. Indeed, the brief 15-minute pulse of DUX4 activity turned a good proportion, up to 17% of the cells, back in the developmental scheme to cells resembling the 8-cell stage.
During 2022, two other groups reported also reprogramming of human cells to the 8-cell stage by using chemical induction. Our report, however, is the only based on entirely genetic reprogramming and with the highest yield of reprogrammed cells. These results will now allow us and other researchers to study many steps of the early human development without the need to use human embryos. Human embryos are available in small numbers as donations by parents undergoing in-vitro fertilization treatments. The earliest stages of human development are now within reach of detailed molecular study in a sound and acceptable manner.
Transient DUX4 expression in human embryonic stem cells induces blastomere-like expression program that is marked by SLC34A2. Yoshihara M, Kirjanov I, Nykänen S, Sokka J, Weltner J, Lundin K, Gawriyski L, Jouhilahti EM, Varjosalo M, Tervaniemi MH, Otonkoski T, Trokovic R, Katayama S, Vuoristo S, Kere J.Stem Cell Reports. 2022 Jul 12;17(7):1743-1756. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2022.06.002. Epub 2022 Jun 30.PMID: 35777358
DUX4 is a multifunctional factor priming human embryonic genome activation. Vuoristo S, Bhagat S, Hydén-Granskog C, Yoshihara M, Gawriyski L, Jouhilahti EM, Ranga V, Tamirat M, Huhtala M, Kirjanov I, Nykänen S, Krjutškov K, Damdimopoulos A, Weltner J, Hashimoto K, Recher G, Ezer S, Paluoja P, Paloviita P, Takegami Y, Kanemaru A, Lundin K, Airenne TT, Otonkoski T, Tapanainen JS, Kawaji H, Murakawa Y, Bürglin TR, Varjosalo M, Johnson MS, Tuuri T, Katayama S, Kere J. iScience. 2022 Mar 22;25(4):104137. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104137. eCollection 2022 Apr 15.PMID: 35402882
